Health Bulletin - December 2022

This Health Bulletin has 2 articles:
Article-1: Alzheimer's Disease
Article-2: Is Heart Attack the Same as Cardiac Arrest?
Alzheimer's Disease
Author: Dr Karthik Ganta, MD, Board Certified Neurologist & Clinical Neurophysiologist, Cumberland Neurology Group, Oak Ridge, TN
Alzheimer's disease is the most common form of dementia.
It is estimated that 1 in 9 people age 65 and older has Alzheimer’s.
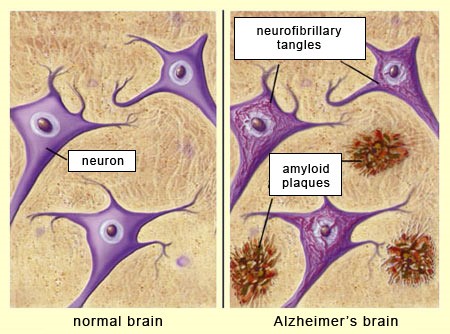
Alzheimer's disease is a brain disease that affects memory, thinking, language, and behavior.
People with Alzheimer's disease lose mental abilities, and the disease gets worse over time.
What are the causes?
This condition develops when a protein called beta-amyloid forms deposits in the brain.
It is not known what causes these deposits to form.
Alzheimer's disease is not hereditary except in rare instances.
What increases the risk?
Age more than 65 years.
Hypertension and Diabetes.
Heart disease and Stroke.
Smoking and excessive alcohol use.
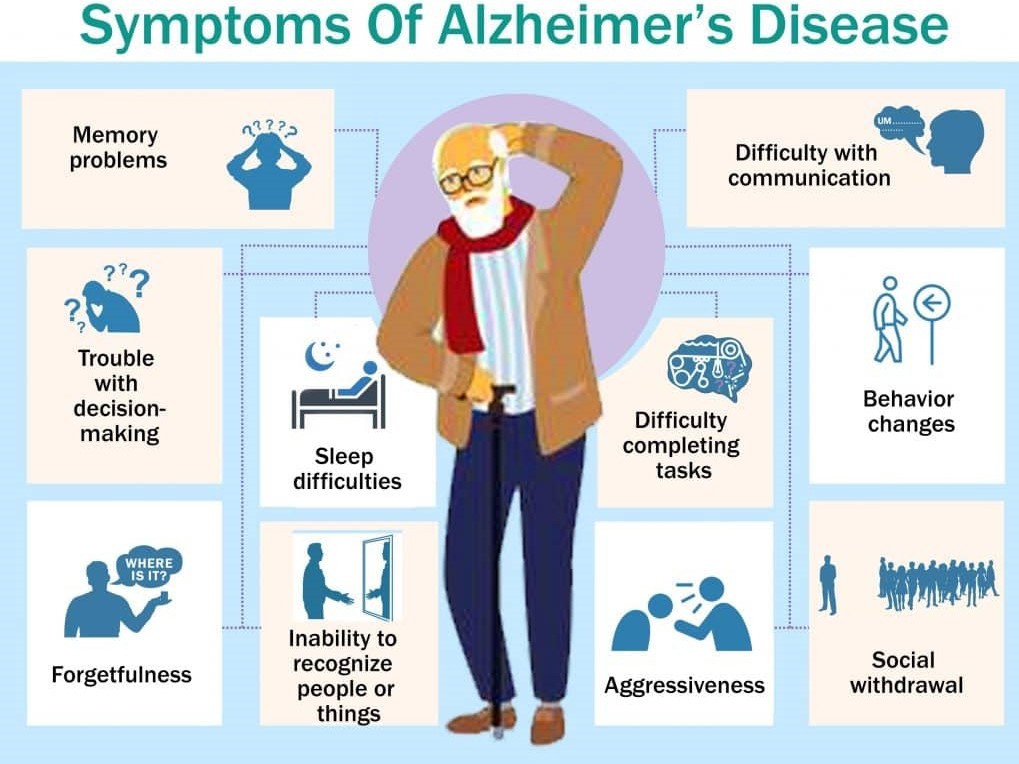
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of this condition may happen in three stages, which often overlap.
Early stage
Minor memory problems, such as forgetting a name, recent conversation, or what you did recently.
Difficulty with paying attention, doing familiar tasks, problem solving, learning new things.
Mild difficulty with driving and managing finances
Can still be independent.
Can still drive, work, and be social.
Moderate stage
Memory loss can start affecting daily life more.
Getting lost while driving or walking. Increasing difficulty managing bills and finances.
Confusion about where you are or what time it is.
Changes in personality, mood, and behavior. You may get anxious, fearful and suspicious.
May start to need care.
Severe stage
Need help with your personal care and daily activities.
Lose awareness of your surroundings.
Changes in physical abilities, including the ability to walk, sit, and swallow.
Increasing behavioral changes like hallucinations.
Problems with urination and bowel movements.
How is this diagnosed?
Diagnosed by a Neurologist (health care provider who specializes in diseases of the nervous system).
A thorough medical history will be taken from patient, their family and friends.
A physical exam and a memory test.
Lab tests, such as blood or urine tests to rule out other causes of memory loss.
CT scan or MRI scan of Brain
In some instances, testing the spinal fluid, PET scan of brain and genetic testing may be undertaken.
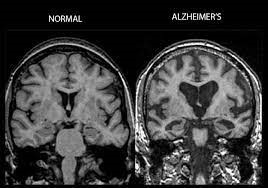
MRI Brain images shows loss of brain tissue (gray areas) and enlargement of brain spaces (black areas) in Alzheimer’s disease
How is this treated?
At this time, there is no treatment to cure Alzheimer's disease or stop it from getting worse.
Medicines may help temporarily. Examples: Donepezil (Aricept) and Memantine (Namenda)
Medicines are used to manage agitation or hallucinations
Family giving care to the patient may experience fatigue. Talk to your doctors if that happens.
Support groups can provide education, emotional support, and information about community resources to family members who are taking care of you.
What can I do?
Take a regular multi-vitamin tablet everyday. Prevagen and Neuriva are NOT clinically proven to improve memory, as advertised on TV.
Avoid taking medicines that can affect thinking, such as pain medicines or sleeping medicines.
Exercise: At least 30 minutes a day for 5 days a week.
Diet: Eat a healthy diet, rich in fresh fruits and uncooked vegetables.
Mediterranean diet has been shown to be helpful.
Sleep: Get at least 7 to 8 hours of sleep per night.
Practice stress-management techniques such as yoga and breathing exercises.
Do not consume tobacco or excess alcohol.
Stay social.
Avoid watching TV or cellphones, using caffeine products during the few hours before you go to bed.
Lifestyle changes can improve memory
General instructions
Talk with your health care provider about whether it is safe for you to drive.
Work with your family to make important decisions, such as advance directives, medical power of attorney, or a living will.
Where to find more information
The Alzheimer's Association: Call the 24-hour helpline at 1-800-272-3900, or visit www.alz.org
Health Bulletin Topic-2
Is Heart Attack The Same As Cardiac Arrest?
Sujeeth R. Punnam, MD, FACC
Interventional Cardiologist, Sutter Health, Stockton, CA
Sudden Cardiac Death Prevention Champion
What is a Heart Attack?
Like every organ in the body, heart also needs blood supply to survive. This blood supply is provided by coronary arteries sitting on the heart. Due to some conditions called risk factors, these arteries develop fatty deposits inside the lumen called as Atherosclerotic Plaques.
When the plaque buildup happens gradually and reaches a point of about 70% or more, the mismatch between the oxygen demand and supply contributes to the heart manifesting symptoms, to warn us and usually it takes the form of chest pain. This is called angina. Occasionally, the plaque ruptures abruptly and suddenly, the blood clots in that area, shutting off the circulation leading to death of the heart cell-That is called heart attack. When the same thing happens in brain, the shut off circulation leads to brain cell death resulting in abrupt weakness or speech impairment- that is called a Stroke.
What is Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) OR Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)?
SCA is a sudden, unexpected failure of heart function leading to impaired organ perfusion. Sudden cardiac arrest is the leading cause of death in adults and 88% of all cardiac arrests happen in people’s homes. Cardiac arrest is reversible if the victim is administered prompt and appropriate emergency care. This generally involves cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), defibrillation to reset the heart's rhythm and advanced life support.
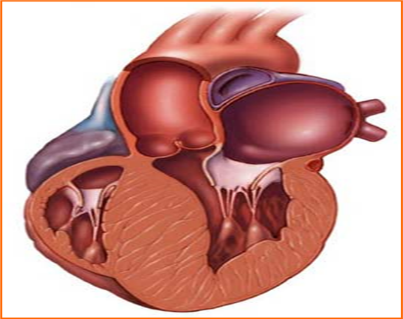
In adults usually Heart Attack is the number one cause for SCA. Most common cause of heart-related sudden death in people under 30 is a condition called Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (picture) where the heart muscle is thicker, scarred but less efficient. It is the most common cause of sudden death in athletes. There are a few other causes too.
Magnitude of the Problem:
Heart disease is the number 1 cause of death among Indians now. About 50% of reported Heart Attacks (MI) in Indian men occurs for people under the age of 50 years, with 25% under the age of 40 years. Some 30% to 40% of cardiovascular deaths occur between 35 and 64 years of age no matter male or female.
What happens when someone has Sudden Cardiac Death?
When heart attack happens, before the muscle is dead, sometimes it could set off an electrical rhythm/storm in the heart muscle called ventricular fibrillation. Early defibrillation of this rhythm is critical to survival from cardiac arrest. Most effective treatment for this is early electrical defibrillation, as probability of successful defibrillation diminishes rapidly over time; and this rhythm tends to convert to a flat line with in a few minutes. While defibrillation is waited on, Basic CPR is needed, however, this by itself is unlikely to convert this abnormal rhythm to a normal rhythm.
Learn Hands-Only CPR. It Saves Lives!
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) is everything that encompasses these basic life saving techniques. At least 100 Compressions per Minute are needed which allows the heart to refill. At least 2 inches
in depth. After each compression, take all weight off the chest. Providing CPR can double a person’s chance of survival from sudden cardiac arrest. If CPR is started within 4 minutes of collapse, and defibrillation is provided within 10 minutes, a person has a 40% chance of survival. As part of advanced CPR, defibrillation should be made available for such victims of SCA.
Early Defibrillation is needed:
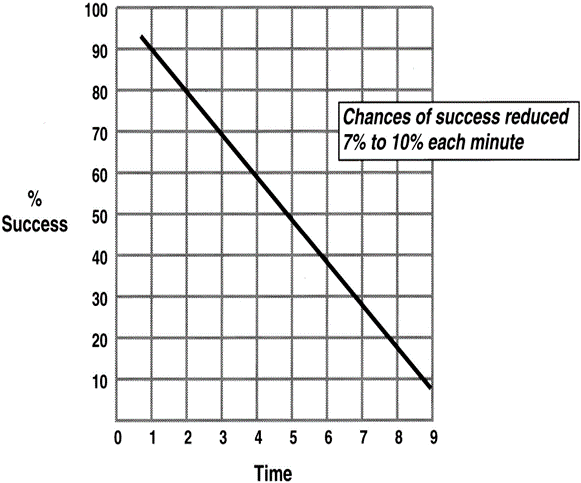
Early defibrillation is critical to survival from cardiac arrest as you can see in this picture showing the chances of success reduced with each passing minute. The first 4 minutes of collapse is called electrical phase, where there is standstill, and any reset can improve the condition and the patient could come out this with no body function impediment. The second phase lasting about 6 minutes is called circulatory phase where if not converted, the blood flow to various body organs starts getting impaired and the effects are seen even if the patient is resuscitated. After 10 minutes, it is called metabolic phase where a cycle of events gets initiated in the body and various internal chemicals are released from the internal organs like intestines, which lead the body into a spiral where nothing else can be done to revive. So, any emergency medical system of a country like 911 in US should have capability to do CPR and early defibrillation. So, learn basic CPR and save lives!
Articles Coordinated By
Sujeeth R. Punnam, MD
Chair, ATA Health Committee
(Dr. Sujeeth R. Punnam is a cardiologist in Stockton, California and is affiliated with multiple hospitals in the area, including Dameron Hospital and St. Joseph's Medical Center-Stockton. He received his medical degree from Kakatiya Medical College NTR and has been in practice for more than 20 years.)

 Join our
Join our